Definition of the term (“What is Chapter 7 of the EU GMP Guide?”)
The EU GMP Guidance, Chapter 7 is a key part of the EU regulatory framework for pharmaceutical manufacturing. This chapter focuses on outsourced activities, including quality control, contract manufacturing and analysis. Chapter 7 of the EU GMP guidelines sets out the responsibilities of pharmaceutical companies when outsourcing certain aspects of production and analysis. It covers various aspects of quality assurance, risk evaluation and regulatory compliance in outsourced activities.
Why is compliance with Chapter 7 important?
Compliance with the EU GMP guidelines, Chapter 7, is crucial for pharmaceutical companies to ensure the safety and effectiveness of their products. Non-compliance can lead to regulatory sanctions and, above all, jeopardize patient safety.
What are the outsourced activities from chapter 7?
This section goes into more detail on the outsourced activities described in chapter 7.
- Types of outsourced activities: Chapter 7 categorizes outsourced activities into different types, such as manufacturing, packaging, labeling and analytical verification. Each species has its own requirements and guidelines.
- Risk evaluation: Before outsourcing an activity, pharmaceutical companies must perform a thorough risk evaluation. This evaluation helps to identify potential risks and ensure that appropriate risk mitigation measures are taken.
- Quality agreements: Quality agreements play a decisive role in outsourcing. They define the responsibilities of both the outsourcing company and the contractor and set out the quality standards that must be met.
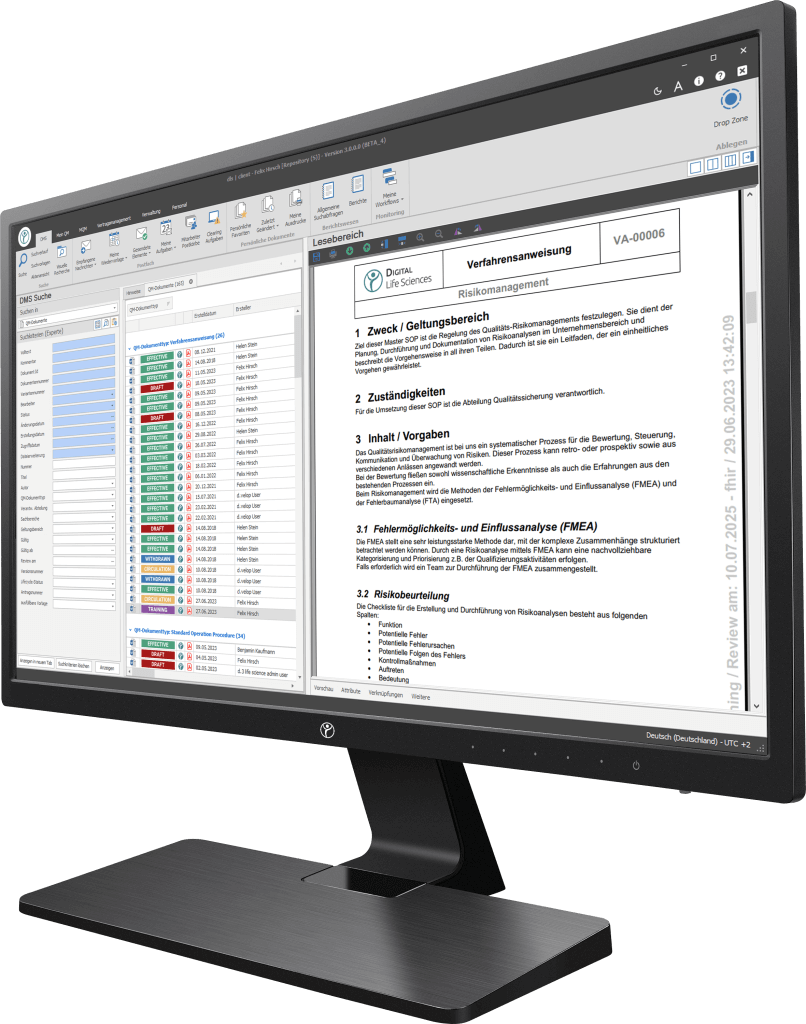
Your path to digitization — Discover our software
Our digitization solutions primarily address document-based processes in manufacturing, production and quality management. The basis of the dls | eQMS is a holistic ECM/DMS system. The ECM/DMS system can be connected to your existing ERP system (e.g. SAP) and thus map almost all document-based processes in the company.
Regulatory requirements
Understanding the regulatory requirements is essential for compliance with the EU GMP guidelines, Chapter 7.
- Regulatory authorities: Pharmaceutical companies need to be aware of the regulatory authorities involved in their outsourced activities. This includes both European and national authorities.
- Documentation: Chapter 7 emphasizes the significance of proper documentation. Detailed records of outsourced activities, quality agreements and risk evaluations must be maintained to demonstrate compliance.
- Audit and inspection: Regular audits and inspections by regulatory authorities are common in outsourced activities. Companies must be prepared to carry out these evaluations and deploy the necessary documentation.
Quality control
Quality control is a crucial aspect of Chapter 7.
- Verification and analysis
Pharmaceutical companies must ensure that outsourced testing and analysis activities are carried out in accordance with the specified standards. This includes the validation of methods and the qualification of devices. - Product release: The responsibility for the release of products lies with the pharmaceutical company. It is important to have clear procedures for the release and certification of batches.
- Change control: Changes to outsourced activities must be carefully managed and documented. Chapter 7 provides notes on how change control should be handled effectively.
Conclusion
In summary, the EU GMP Guidance, Chapter 7 is an important part of the EU regulatory framework for pharmaceutical manufacturing. Compliance with this chapter is crucial to ensure the quality, safety and effectiveness of medicinal products. By following the guidelines set out in Chapter 7, pharmaceutical companies can confidently manage the complexities of outsourced activities.
Start your digital transformation with our powerful, modular software solutions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the main objective of the EU GMP Guidance, Chapter 7?
The main objective is to ensure the quality, safety and effectiveness of medicinal products by deploying guidelines for outsourced activities.
Who must comply with Chapter 7 of the EU GMP guidelines?
Pharmaceutical companies involved in outsourced activities, including contract manufacturing and analysis, must comply with Chapter 7.
What are the most important components of a quality agreement?
Among other things, a quality agreement should define responsibilities, quality standards and procedures for change control.
How often should audits of outsourced activities be performed?
Audits should be carried out regularly, with the frequency determined by the risk associated with the outsourced activity.
Can outsourcing lead to a reduction in product quality?
Yes, if not properly managed, outsourcing can pose risks to product quality. Chapter 7 of the EU GMP guidelines therefore emphasizes the significance of risk evaluation and quality agreements.
What happens in the event of non-compliance with Chapter 7?
Non-compliance may result in regulatory sanctions, including suspension of manufacturing licenses and product recalls.
What is the key principle in Chapter 7 of the EU GMP Guidance in relation to outsourced activities?
The principle states that all GMP processes and their support that are outsourced must be adequately defined, agreed and controlled.
What are the requirements for the written contract between the contractor and contracting entity for outsourced activities?
The written contract should include all responsibilities and agreements made between the contractor and the contracting entity in relation to the outsourced activities.
What is the contracting entity’s task in connection with outsourced activities prior to outsourcing?
Before outsourcing, the contracting entity is responsible for assessing the suitability and competence of the contractor.
What does the contracting entity need to ensure when it comes to controlling outsourced activities?
The contracting entity must ensure that control processes are in place for the assigned activities and that the contractor’s compliance with GMP principles is guaranteed.
What is the contractor’s responsibility with respect to computerized systems in outsourced activities?
The Contractor must ensure that the services it provides, in particular computer-based systems, always meet the requirements set and are suitable for the intended purpose.
When can outsourced activities and the concluded contract be subject to inspection by the competent authority?
Outsourced activities and the contract concluded may be subject to inspection by the appropriate authority at any time, and the contractor should be aware of this possibility.
