Definition of the term ("What is GMP?")
GMP stands for “Good Manufacturing Practice”. Thus, GMP includes guidelines and regulations that must always be followed when companies are involved in the manufacturing and handling of products that, in the broadest sense, can affect people’s quality of life. These include, for example, medicinical products and foodstuffs, but also cosmetics. Since quality deviations can have a direct impact on human health, quality assurance plays a central role, especially in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Why is GMP important?
GMP is critical for several reasons. It protects consumers by ensuring that products are safe to consume. It maintains the integrity of the manufacturing process and reduces the risk of contamination or deviations. And GMP compliance is often a legal requirement in many industries.
The main principles of GMP
- Documentation and recording: One of the fundamental principles of GMP is thorough documentation. Each step of the manufacturing process must be documented and kept on file to enable traceability and accountability.
- Quality control: Quality control is at the heart of GMP. It involves strict testing and the inspection of products to ensure they meet predefined specifications. Deviations from these standards result in corrective actions.
- Training of staff: The persons involved in the manufacturing process play a crucial role. Proper training ensures that employees are aware of and comply with GMP requirements.
- Maintenance of plants and equipment: Regular maintenance of manufacturing facilities and equipment is critical to prevent contamination and to ensure product consistency.
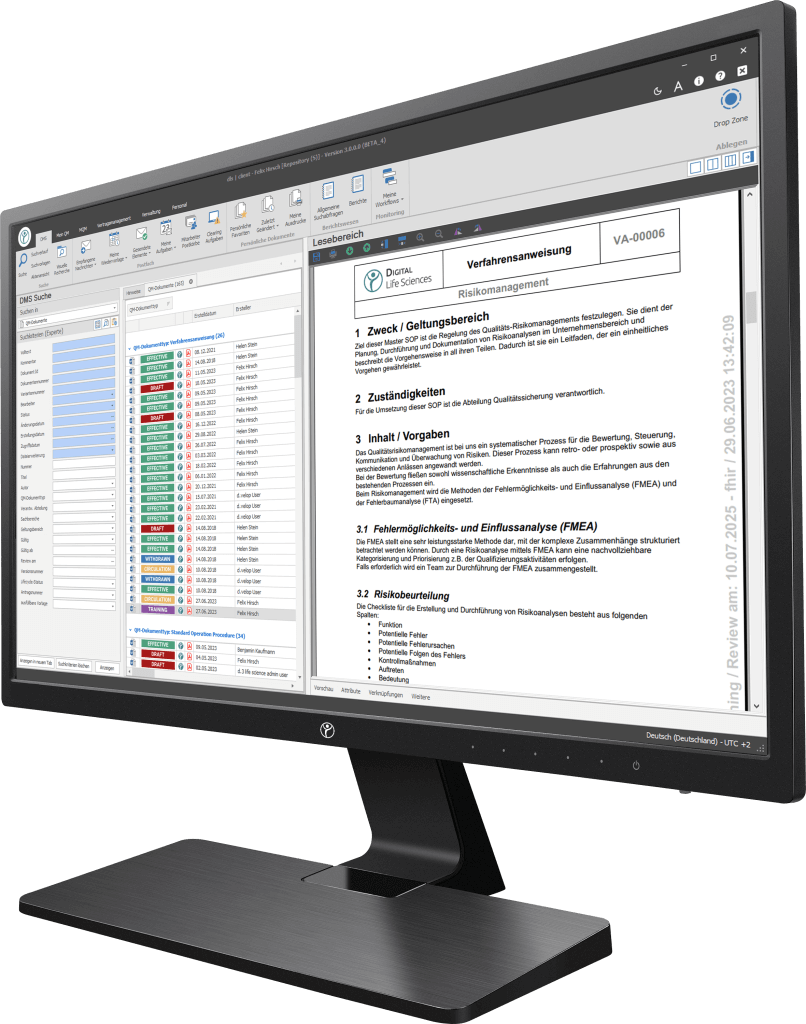
Your path to digitisation - Discover our software
Our digitisation solutions primarily address document-based processes in manufacturing, production and quality management. The basis of the dls | eQMS is a holistic ECM/DMS system. The ECM/DMS system can be connected to your existing ERP system (e.g. SAP) and thus map almost all document-based processes in the company.
GMP in different industries
GMP is a diverse concept that is used in various industries:
- Pharmaceuticals: In the pharmaceutical industry, GMP is a cornerstone. It guarantees that medicines are safe and effective, giving consumers confidence in their treatments.
- Food production: GMP is also of critical significance in the food industry. It ensures the quality and safety of food products and prevents contamination and foodborne illness.
- Cosmetics: Cosmetics are also subject to GMP regulations. This ensures that the skincare and beauty products that consumers use meet the highest standards.
Conclusion
In a world where product quality and safety are top priorities, GMP stands as a guardian. It is a set of principles that ensure manufacturing processes meet the highest standards and benefit consumers and industries alike. By implementing GMP, companies do not only meet regulatory requirements, but also build trust with their customers and promote long-term success.
Start your digital transformation with our powerful, modular software solutions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the consequences of non-compliance with GMP regulations?
Failure to comply with GMP regulations can result in product recalls, legal penalties, reputational damage and, in extreme cases, consumer harm.
Is GMP a global standard?
Yes, GMP principles are recognised and applied worldwide, although specific regulations may vary by country or region.
How can a company implement GMP effectively?
The effective implementation of GMP requires thorough training, documentation, quality control, and continuous improvement processes.
Are GMP regulations static or do they evolve over time?
GMP regulations are not static. They evolve to adapt to changing industry trends, technological advances, and emerging risks.
Can small companies comply with GMP regulations?
Yes, GMP principles can be adapted to the size and complexity of a company. Small businesses can also benefit from complying with these standards to ensure product quality and safety.
How is a quality management system relevant to GMP compliance?
Companies in the aforementioned industries must implement GMP-compliant quality management in order to ensure the required product quality and to meet the legal requirements for marketing the products. A GMP-compliant quality management system consists of several elements, such as document management for specification documents. Requirements include that specification documents such as work instructions, process instructions, forms, etc. must be version-controlled and subject to a defined life cycle. These documents must also have an audit trail that logs all actions, especially changes. Without compliance with GMP regulations, no company will be granted permission to manufacture pharmaceutical products.

