Definition of the term (“What is an audit?”)
An audit checks whether requirements, processes and guidelines comply with required standards or norms. Due to the high significance of quality, audits are often carried out as part of a quality management. This differentiates between two types of audits within the static and dynamic quality management.
In static quality management, there are audits with an audit character that provide evidence of contractual agreements and are only carried out once. In dynamic quality management, on the other hand, audits are used to record development trends and provide the originators of changes with feedback on the impact of the measures introduced.
An audit can take place either as an internal audit for self-assessment or as an external audit. The external audit differs from the internal audit in that it is a certified requirement in quality management and is carried out by recognized bodies. This is followed, for example, by official certification.
The audit trail should also be mentioned in connection with the audit. An audit trail is a procedure in which both attempted and executed actions by persons are monitored and electronically documented over a period of time. In addition, the audit trail can also represent a chronological sequence of actions, processes and system states that can be traced back through traces such as bookings.
Your path to digitisation - Discover our software
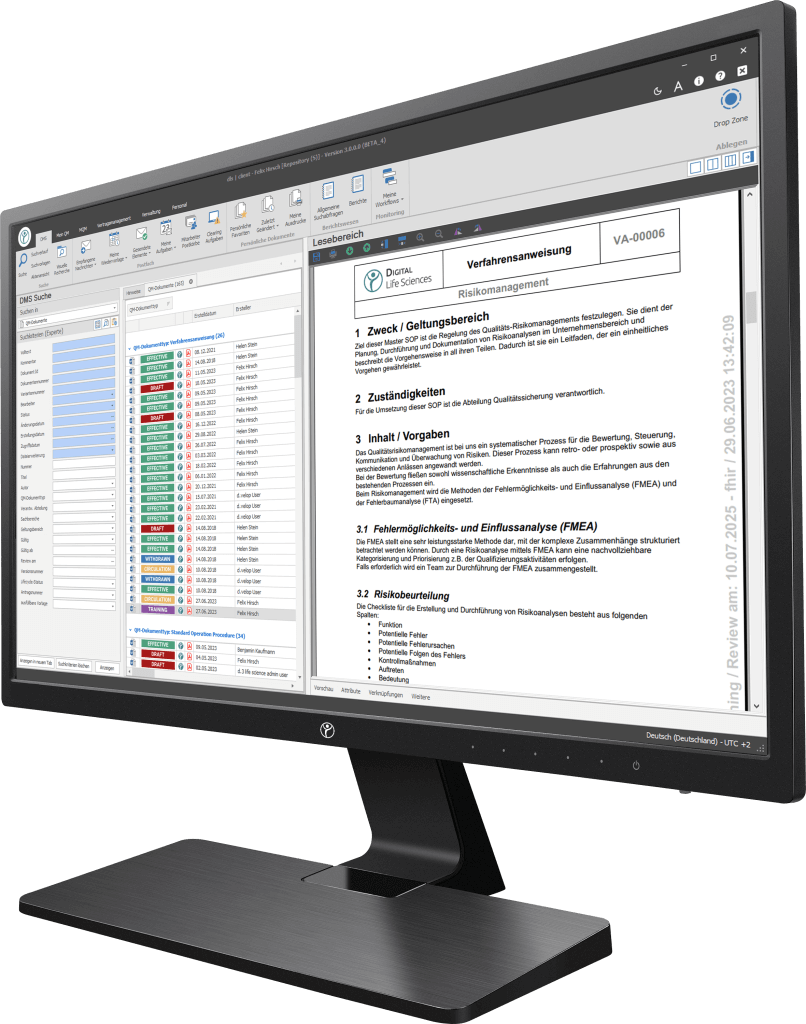
Our digitisation solutions primarily address document-based processes in manufacturing, production and quality management. The basis of the dls | eQMS is a holistic ECM/DMS system. The ECM/DMS system can be connected to your existing ERP system (e.g. SAP) and, thus, map almost all document-based processes in the company.
What is an audit in quality management?
An audit in quality management is a systematic, independent and documented review to determine whether the activity profiles and results are in accordance with the planned agreements. The aim of this process is to evaluate the suitability and effectiveness of a quality management system (QMS) and, if necessary, to identify potential for improvement.
Types of audits
Internal audits
Internal audits are mainly used for self-assessment and continuous improvement of the quality management system within a company. They are carried out by internal employees who are specially trained for this purpose.
External audits
An external audit is carried out by independent, external organizations to confirm that a company complies with the specified standards and certifications. External audits are often a precondition for certification in quality management and are carried out by recognized bodies.
Supplier audit: A supplier audit is a specialized type of external audit in which the quality and conformity of a company’s suppliers is evaluated. The frequency with which a supplier audit is carried out can vary, but should be carried out regularly, often annually or after a risk analysis of the supplier.
Self-assessment as a synonym in quality management
The term “self-assessment” is often used synonymously with internal audit. It describes the process of internal audits for the continuous analysis and improvement of company processes. This type of audit provides companies with a clear overview of their own processes and helps to identify and eliminate internal weak points.
Summary of the different types of audits
There are several types of audits that can be carried out in the section of quality management:
- System audit: Focus on the management system to ensure that the system elements are effectively implemented and maintained.
- Process audit/procedure audit: Review specific processes to ensure that they meet the defined requirements and are implemented effectively.
- Compliance audit: Checking conformity with a set of rules.
- Certification audit: Conducted by independent auditors from an accredited certification body to obtain formal certification.

