Definition of the term (“What is CAPA?”)
A CAPA (Corrective and Preventive Action) is a measure within the quality management system (QMS) and is part of GMP compliant operations. This analyzes actual faults or deviations in a structured manner (corrective action) or implements preventive actions.
Compared to other QMS standards such as ISO 9001, CAPA is a crucial process for ensuring product and process orientation, especially in the pharmaceutical industry. CAPA is not so much a continuous improvement process, but focuses on eliminating any deviations from requirements based on the applicable legal regulations and technical standards for the safety of medicinal products and medical devices.
Why is CAPA important?
- Ensuring quality: Quality is the cornerstone of any successful business. CAPA measures play a central role in maintaining and improving product and service quality. By addressing problems promptly and systematically, companies can deliver consistent quality to their customers.
- Compliance with legal requirements: In today’s highly regulated industries, compliance with government standards and regulations is non-negotiable. CAPA helps companies comply with regulations by identifying and resolving deviations from industry standards. This aspect of compliance is particularly important for companies in the pharmaceutical industry.
What are the components of CAPA?
- Root cause analysis (RCA): Root cause analysis (RCA) is the first step in the CAPA process. It involves a thorough examination to determine the causes of a problem. Identifying the root cause is crucial for implementing effective corrective and preventive actions.
- Corrective measures: Corrective actions are specific measures taken to address the immediate problem or nonconformity. These measures are aimed at eliminating the problem and preventing its recurrence.
- Preventive actions: Preventive actions are proactive measures designed to prevent the occurrence of similar problems in the future. They include process improvements, trainings and ongoing monitoring.
Your path to digitization — Discover our software
Our digitalization solutions primarily address document-based processes in manufacturing, production and quality management. The basis of the dls | eQMS is a holistic ECM/DMS system. The ECM/DMS system can be linked to your existing ERP system (e.g. SAP), thus enabling you to implement almost all document-based processes in your company.
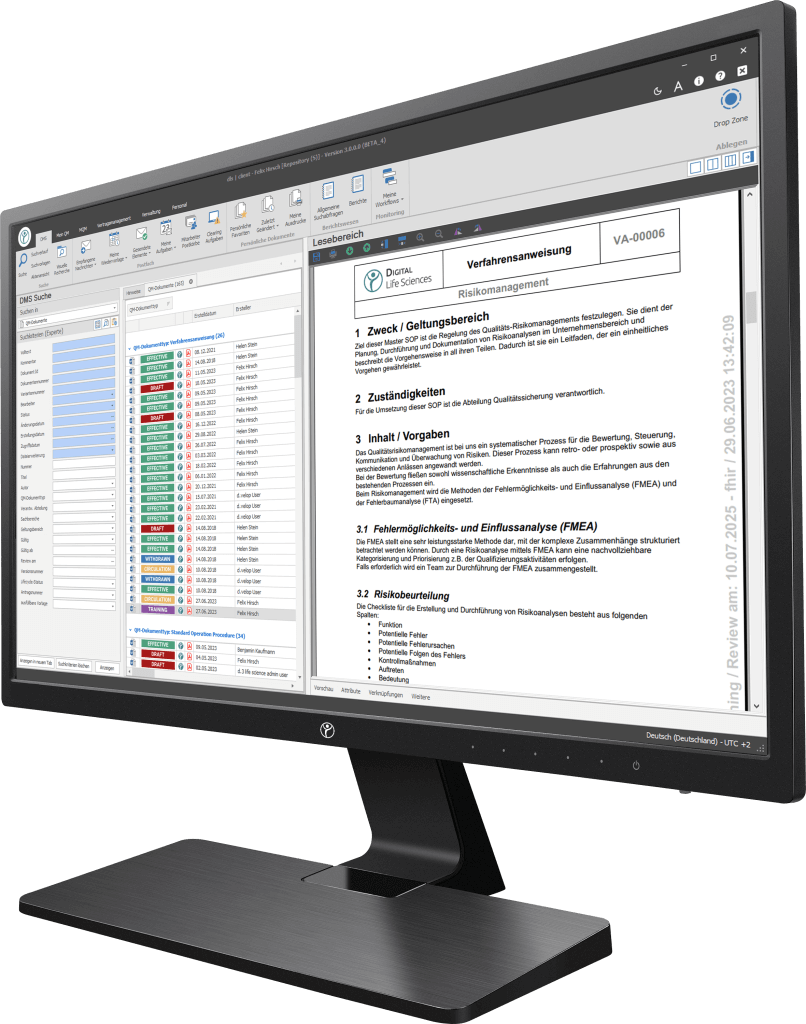
How is a CAPA introduced?
Documentation and record keeping: A thorough documentation of CAPA activities is critical for transparency and compliance. Detailed records of investigations, measures and results are essential.
CAPA process description: A precise and detailed CAPA process description is important to ensure that all employees understand the steps and requirements and implement them correctly.
What challenges are there in CAPA implementation?
- Resistance to change: CAPA implementation often requires changes to existing processes. Employee resistance to change can reduce the effectiveness of CAPA initiatives.
- Limited Resources: CAPA activities can be resource intensive. Organisations need to deploy the necessary resources to ensure the successful implementation of corrective and preventive actions. This can be counteracted with the help of suitable CAPA software.
Conclusion
In summary, corrective and preventive action (CAPA) is an important tool for organisations seeking to improve their processes, maintain quality, and meet regulatory requirements. By understanding the components of CAPA and overcoming the challenges of implementation, organisations can achieve operational excellence. When you embed CAPA as a culture in your company, you pave the way for continuous improvement and long-term success.
Start your digital transformation with our powerful, modular software solutions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How often should CAPA procedures be reviewed?
CAPA procedures should be reviewed regularly, at least annually, to ensure they remain effective and updated.
Are there software solutions for managing CAPA procedures?
Yes, various software solutions can streamline CAPA management and make it more efficient and organized. You can find a qualified solution here, for example.
Can CAPA also be applied in industries other than manufacturing?
Absolutely. CAPA principles can be applied in any industry or sector that aims to improve processes and maintain quality.
What role does top management play in the implementation of CAPA?
Senior management should lead and support CAPA initiatives and ensure that they are aligned with the company’s strategic goals.
How can organisations measure the effectiveness of their CAPA efforts?
The effectiveness of CAPA efforts can be measured by tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) such as reduced defect rates, improved compliance and customer satisfaction.
Where does the term CAPA come from?
The term CAPA originates from medical device regulations and was also described in the original system elements in ISO 9001, ISO 13485, and FDA 21.
When was CAPA first introduced?
CAPA was first introduced in 2006 via the “Quality System Guidance” of the FDA. Since 2008 it is an element of a QMS based on the ICH guideline Q10 Pharmaceutical Quality Systems. In the further process, the guideline was adopted in the newly added 3rd part of the EU GMP guideline.
What makes CAPA (Corrective and Preventive Action) an indispensable part of quality management in the pharmaceutical industry?
CAPA is indispensable in quality management in the pharmaceutical industry because it helps to maintain product quality at a high level and meet regulatory requirements. Systematic CAPA measures allow errors that occur (corrective action) to be identified and permanently rectified and future errors (preventive action) to be avoided. This ensures that all products are safe and effective, which is essential to protect patient integrity and comply with government regulations.
What key steps and elements should a detailed CAPA process description include?
A detailed CAPA process description should include several key steps:
- Recording of deviations: Collection and documentation of errors or deviations that have occurred.
- Root cause analysis: Implementation of a Root Cause Analysis (RCA) to identify the root causes of the problem.
- Development of the Corrective Action Plan: Planning and implementation of specific corrective actions to resolve the problem immediately.
- Implementation of preventive actions: Identification and implementation of preventive actions to avoid future errors.
- Review and monitoring: Monitoring the effectiveness of the implemented measures and readjusting them if necessary.


